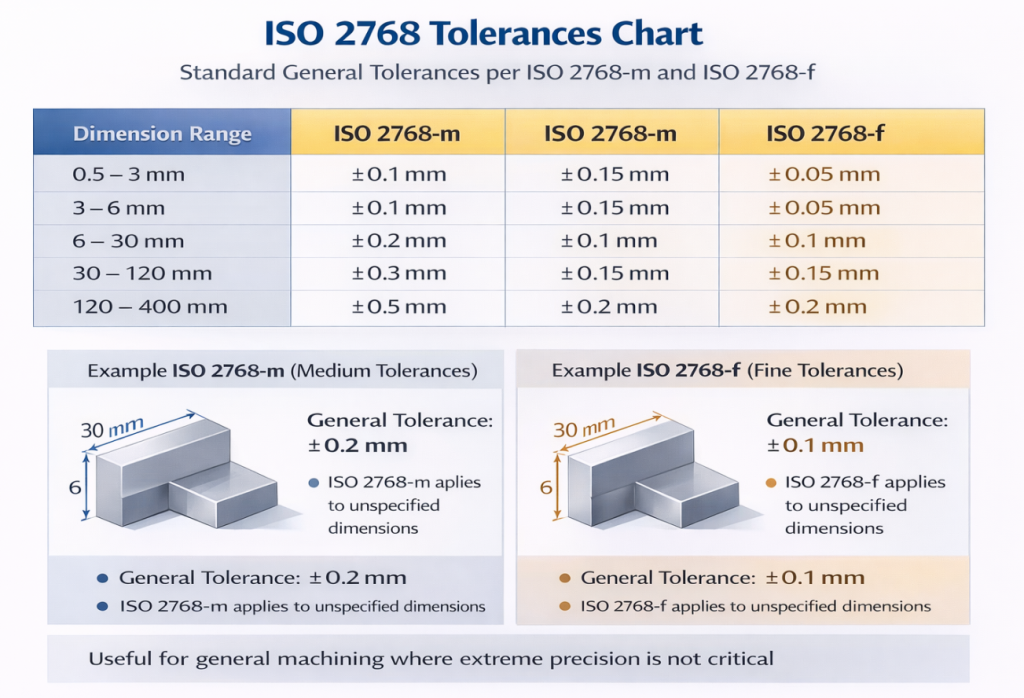
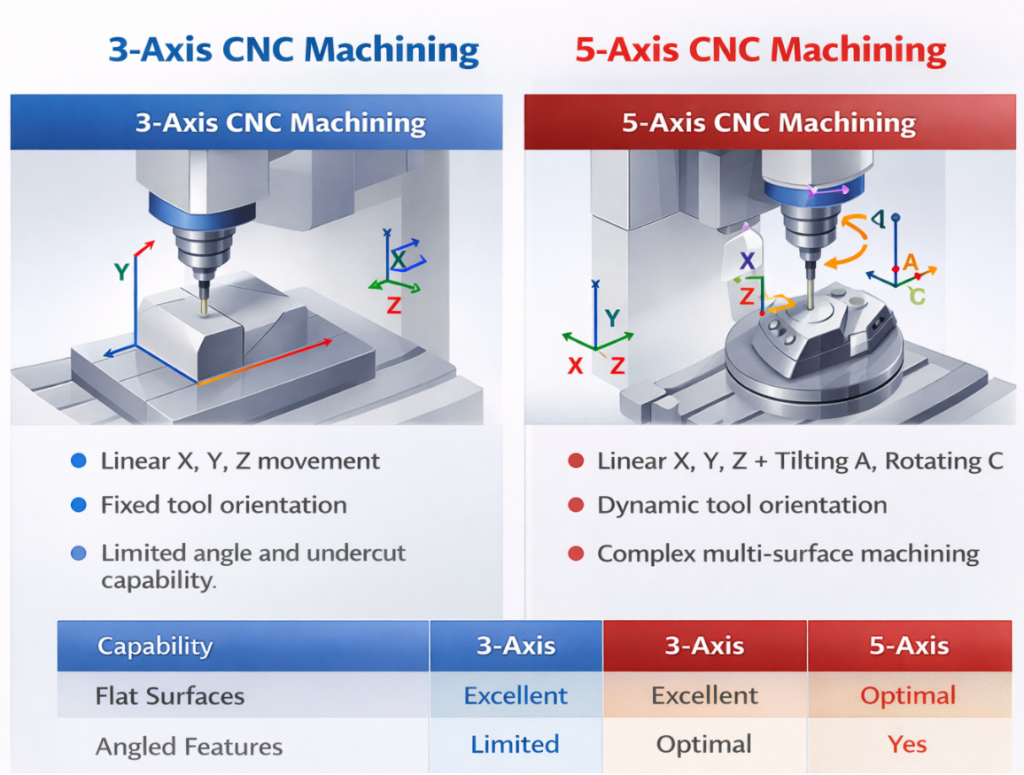
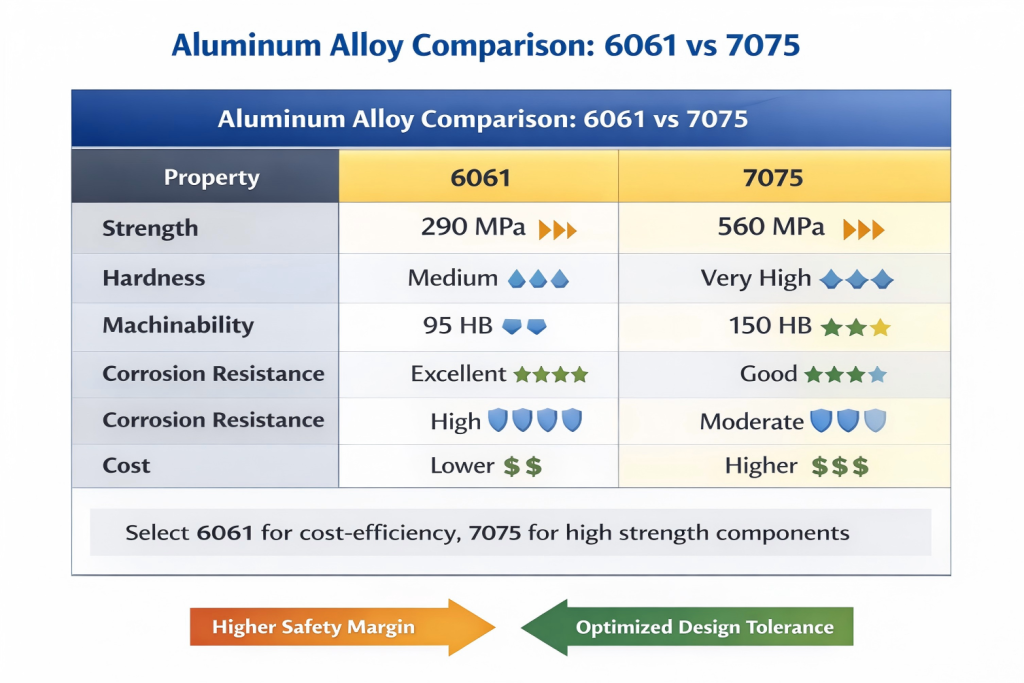
Abstract
This article provides a profound analysis of the CNC machining equipment matrix, systematically combing through the technical essentials of three core components: control systems, servo systems, and execution mechanisms. Focusing on star brands such as Siemens, Fanuc, Mitsubishi, and Haas (with official website links), it reveals how their technological innovations drive improvements in precision, efficiency, and flexibility in modern manufacturing. This serves as an authoritative reference for manufacturing professionals to optimize production configurations and grasp technological trends.
1. Control Systems: The “Intelligent Brain” of CNC Machining
1.1 Siemens
Siemens control systems are renowned for their high-speed instruction processing capability (up to 1,000 blocks per second), which accurately parses complex machining programs to ensure stability and coordination in multi-axis (multi-axis simultaneous) machining. Their advantages are particularly prominent in the aerospace industry. For example, when machining high-precision turbine blades, seamless compatibility with advanced CAM software achieves micron-level precision control, while supporting real-time working condition monitoring to significantly reduce machining errors and equipment failure rates.
1.2 Fanuc
Fanuc control systems are famous for their high reliability and intelligent operation interfaces, widely used in mass production of automotive parts. Their real-time error compensation technology can dynamically adjust tool paths during batch processing of components such as gearbox housings, ensuring dimensional consistency for each product. Even under long-term continuous operation, it maintains a positioning accuracy of ±0.01mm, making it an ideal choice for automated production lines.
2. Servo Systems: The “Core Engine” Driving Precision Motion
2.1 Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi servo systems have become the first choice in the medical device machining field with ±0.001mm ultra-high positioning accuracy and millisecond response speed. In the milling of orthopedic implants (such as joint prostheses), it can precisely execute micro-feeding commands, together with dynamic torque compensation technology, to avoid processing deformation caused by uneven hardness of the material, to ensure that the surface roughness of the implant reaches Ra0.2μm or less, and to meet the requirements of biocompatibility.
3. Execution Mechanisms: Key Units Endowing Machining with “Physical Kinetic Energy”
3.1 Haas
Haas machine tools are equipped with a 24,000rpm high-speed spindle and a large-capacity intelligent tool magazine (30-120 tool capacity), balancing high-efficiency rough machining and precision finishing. In aluminum alloy mold manufacturing, the high-speed spindle can achieve a feed rate of over 5,000mm per minute to quickly remove excess material. Combined with the tool magazine’s automatic tool change and tool life management functions, it can reduce downtime during complex cavity machining and increase overall production efficiency by more than 30%.
4. Synergy Schematic of the Equipment Matrix
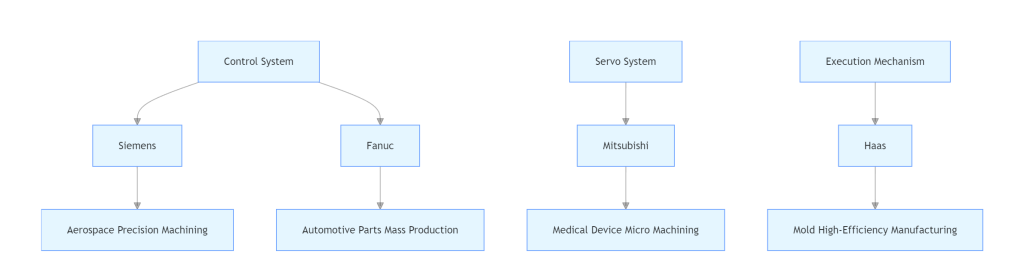
graph TD <br>A[Control System] --> B[Siemens] <br>A --> C[Fanuc] <br>D[Servo System] --> E[Mitsubishi] <br>F[Execution Mechanism] --> G[Haas] <br>B --> H[Aerospace Precision Machining] <br>C --> I[Automotive Parts Mass Production] <br>E --> J[Medical Device Micro Machining] <br>G --> K[Mold High-Efficiency Manufacturing] Conclusion
The optimized configuration of the CNC machining equipment matrix essentially represents a systematic balance of “control precision-drive capability-execution efficiency.” Brands like Siemens and Fanuc continue to expand the technical boundaries of each component through continuous innovation. For manufacturing enterprises, selecting suitable brands and models from the equipment matrix based on their own processing needs (such as precision grade, material characteristics, and production scale) can not only improve single-piece machining quality but also build an efficient and intelligent manufacturing ecosystem through automated linkage and data interoperability, gaining a competitive edge in the fierce market.